Difference Between MonoFacial And Bifacial Solar Panels. Welcome To SolarPrice Here You will get Knowledge Related To Solar Panels And Solar Products As Well As Solar Batteries. Today We Are Going To Discuss the Difference Between Monofacial And Bifacial Solar Panels.
Monofacial– The Time Of Solar Which produces energy (Electricity) From One Side Of The Solar Panel
Bifacial Solar Panel- A Type Of Solar Panel That produces electricity from Both Sides Of a Solar Panel Called a Bifacial Solar Panel.
Here You Well Get More Such Content On SolarPrice.
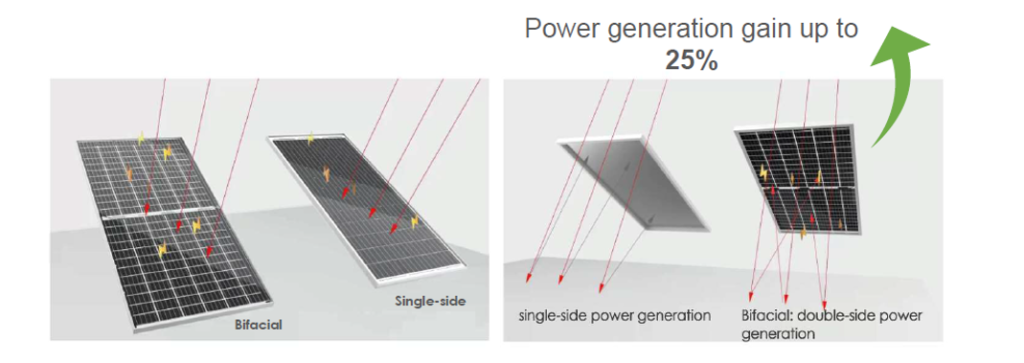
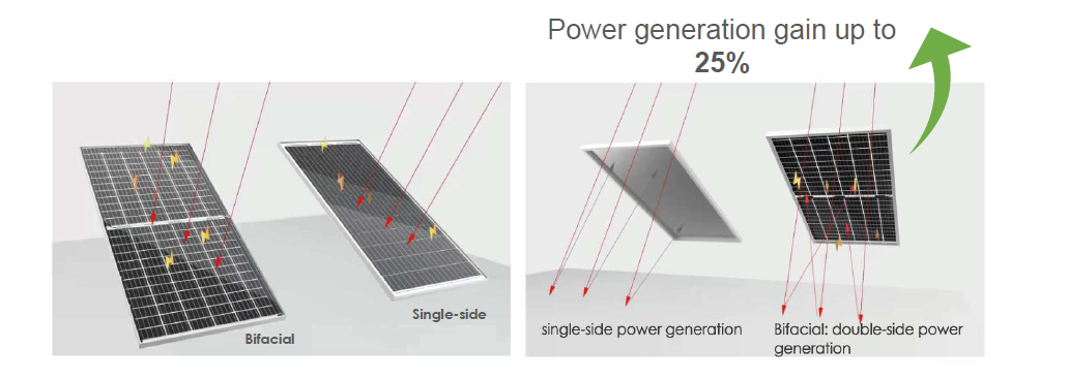
MonoFacial Vs Bifacial Solar Panels
Monofacial and bifacial solar panels are two types of photovoltaic (PV) panels used to convert sunlight into electricity, but they differ in their design, efficiency, and applications. Here are the main differences between them:
Monofacial Solar Panels
- Design
- Have photovoltaic cells on only one side (the front).
- The back side is usually opaque and covered with a protective layer.
- Energy Generation:
- Generate electricity from sunlight that directly hits the front side of the panel.
- Efficiency:
- Typically have lower overall efficiency compared to bifacial panels because they can only capture sunlight from one direction.
- Installation:
- Can be mounted in various orientations, but are commonly placed at a fixed tilt facing the sun.
- Suitable for rooftop installations and ground-mounted arrays.
- Cost:
- Generally less expensive to manufacture and install compared to bifacial panels.
Bifacial Solar Panels
- Design
-
- Have photovoltaic cells on both sides (front and back).
- The back side is transparent or semi-transparent, allowing light to pass through or reflect from surfaces beneath the panel.
- Energy Generation
-
- Generate electricity from sunlight that hits both the front and the back sides of the panel.
- Can capture reflected and diffused light from surfaces like the ground, water, or rooftops.
- Efficiency
-
- Typically have higher overall efficiency due to their ability to capture sunlight from both sides.
- Can produce up to 30% more energy compared to monofacial panels, depending on the installation environment.
- Installation
-
- Best installed in locations where the rear side can capture significant reflected light.
- Commonly used in ground-mounted arrays with a reflective surface underneath or vertically mounted in certain applications.
- Cost
-
- More expensive to manufacture and install than monofacial panels.
- Higher initial cost can be offset by increased energy production and efficiency over time.
Applications
- Monofacial Solar Panels: Suitable for residential rooftop installations, commercial buildings, and areas where only direct sunlight exposure is practical.
- Bifacial Solar Panels: Ideal for large-scale solar farms, commercial installations with reflective roofing materials, and environments where maximizing energy output is crucial.